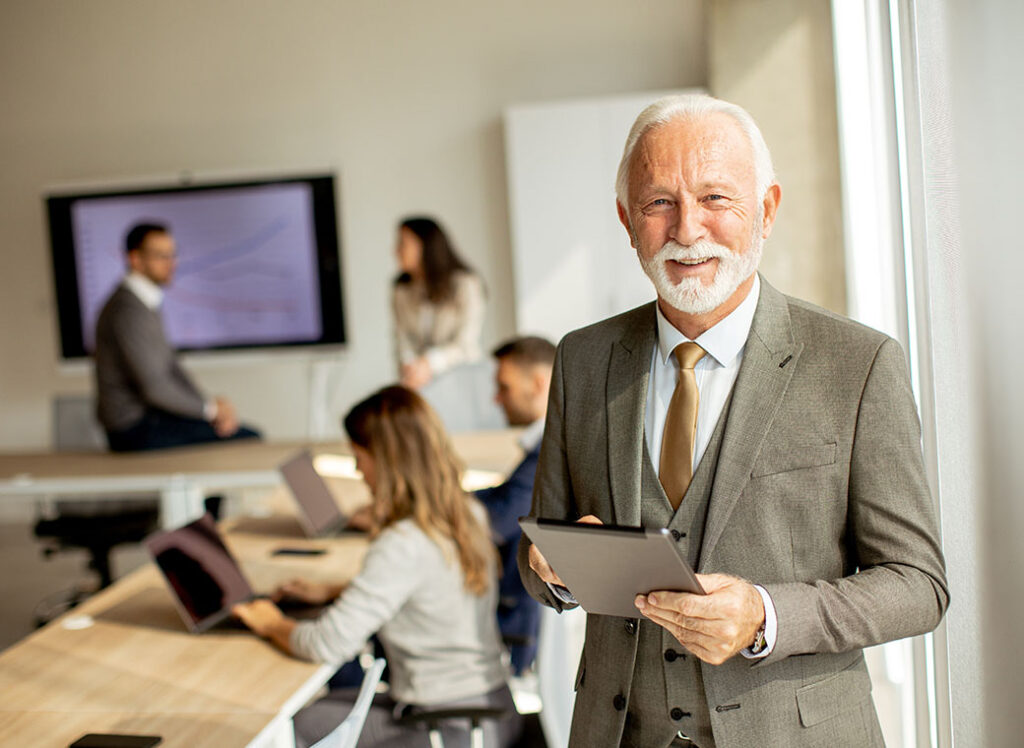
What Is Business Valuation and Why Is It Crucial for Selling Your Business?
Determining an accurate business valuation is the essential first step in any sale. It establishes a fair asking price, builds buyer confidence, and lays the groundwork for honest negotiations. Without a proper valuation, sellers risk setting a price too high or too low, which can delay the sale or result in lost value. Business valuation considers factors such as cash flow, revenue, market trends, industry conditions, and future earning potential. This process not only highlights strengths like operational efficiency and sound financial reports but also pinpoints areas for improvement.
Securing an independent or professional valuation reinforces credibility and helps achieve the best possible sale price.
What Are the Main Business Valuation Methods?
There are three primary methods to value a business:
• Asset-Based Approach: This method calculates a company’s net asset value by subtracting liabilities from the total assets.
• Earnings Value Approach: It focuses on historical and projected cash flows, often employing discounted cash flow (DCF) analysis to estimate present value using an appropriate tax rate and market risk premium.
• Market Value Approach: This method compares the business with similar transactions in the same industry, relying on real-life data to set benchmarks.
Each method has its advantages and limitations, and understanding all three provides a well-rounded picture of the business’s worth.
How Do Industry and Market Conditions Affect Business Valuation?
Market dynamics significantly influence a business’s final valuation. Economic trends, competitive landscapes, consumer behavior, and technology changes all contribute to shaping market value. In booming sectors, such as technology, companies may be valued on both current performance and future growth potential. Conversely, in industries facing downturns or heavy regulation, expectations must be adjusted accordingly. Regional factors, such as a strong local business climate, can also elevate a company’s value. Buyers use publicly available analytics and comparables to determine a fair asking price, making a solid valuation even more critical.
How Can You Get a Professional Business Valuation?
Engaging a professional valuationexpert or a certified financial adviser is a reliable way to obtain an unbiased estimate of your business’s worth. These professionals use advanced financial models and relevant market data to produce comprehensive reports. Their analysis not only validates your price but often offers recommendations to increase market value before the sale. Choosing an expert with a proven track record, particularly in small to medium-sized enterprises, ensures that the valuation accurately reflects both market conditions and internal performance.
What Tools and Resources Help Estimate Business Value?
Business owners have access to a range of tools to get initial valuation estimates. Online calculators allow you to input revenue, profit, and industry multipliers to generate a ballpark figure. Additionally, industry reports, financial analysis software, and benchmarking studies provide insights into market trends and buyer expectations. These resources help establish a realistic asking price and identify operational, legal, or financial adjustments that can further enhance business value.
How Do You Prepare Your Business for Sale to Maximize Value?
Proper preparation is key to attracting buyers and achieving a high sale price. This involves a thorough evaluation and improvement of financial records, legal documents, and operational systems. A well-prepared business reduces buyer uncertainties and strengthens your negotiation position.
What Financial Steps Should You Take Before Selling?
Financial preparation starts by cleaning up your financial statements. Ensure that revenue, expenses, cash flow, and profit analyses are accurate and clearly documented. This may involve hiring a financial adviser to audit records, correct discrepancies, and optimize tax returns. Presenting audited statements for the past few fiscal years demonstrates stability and clarifies the business’s profitability, giving buyers confidence in its future performance.
How Do You Organize Legal Documents and Contracts?
Legal readiness is equally important. Organize all relevant documents, such as lease agreements, employment contracts, intellectual property registrations, vendor agreements, and any pending litigation records. Working with an attorney who specializes in mergers and acquisitions can ensure that all contracts are updated and any legal issues are resolved in advance. A well-organized document repository accelerates the due diligence process and reassures buyers of the company’s compliance and governance standards.
How Can You Identify and Highlight Your Business’s Strengths and Weaknesses?
Conduct a thorough self-assessment using a SWOT analysis (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats). Document key strengths like high profit margins, strong brandreputation, experienced management, and innovative technology. At the same time, identify areas such as outdated systems or operational inefficiencies that may need improvement before listing the business. Addressing these areas not only boosts overall performance but can significantly enhance the final valuation.
What Are Best Practices for Streamlining Business Operations?
Efficiency in operations is a major selling point. Implementing robust workflow systems, updating software and technology, and streamlining supply chain logistics can all enhance productivity. Regular employee performance reviews and targeted training programs further improve operational efficiency. Clear documentation of standard operating procedures (SOPs) and key performance indicators (KPIs) provides transparency to buyers, reassuring them that the business will continue to run effectively post-sale.
How Do You Market Your Business to Attract the Right Buyers?
Effective marketing increases the chances of finding a qualified and motivated buyer. A targeted strategy not only showcases your business’s strengths but also ensures confidentiality throughout the sales process.
What Is a Confidential Information Memorandum (CIM) and How Do You Create One?
A Confidential Information Memorandum (CIM) is a vital marketing tool that provides potential buyers with a detailed summary of your business. It generally covers an overview of the company, financial performance, market analysis, operational details, and growth opportunities. The document should be professionally prepared and tailored to address the interests of your target buyer. A well-crafted CIM, often created with the assistance of business brokers or marketing consultants, can significantly boost buyer interest.
How Do You Identify and Target Potential Buyers?
Identifying the right buyers is crucial. Potential bidders include private equity firms, strategic investors, competitors, and individuals looking to expand their current operations. Effective buyer targeting involves thorough market research and developing detailed buyer profiles based on financial capacity, industry expertise, and strategic alignment. Using professional buyer databases, industry networks, and advisory services can help compile a list of qualified prospects for direct outreach and targeted advertising.
What Marketing Strategies Are Effective for Selling a Business?
A mix of marketing strategies tends to work best. Online business listings on reputable marketplaces increase visibility, while engaging a seasoned business broker can tap into a broader network of qualified buyers. Social media marketing, targeted email campaigns, and participation in industry events or trade shows can also amplify your reach. The goal is to drive competition and attract offers that align well with your desired sale price—all while maintaining the confidentiality of sensitive information.
How Can You Maintain Confidentiality During Marketing?
Maintaining confidentiality is essential to protect your business’s operational stability. Use non-disclosure agreements (NDAs) and anonymize your business’s identity in initial communications and listings. Only share critical details with pre-qualified buyers under strict confidentiality protocols. Business brokers can manage this process effectively by vetting potential buyers and controlling the flow of information, thereby minimizing risks such as employee disruption or unwanted competitive insights.
What Is the Due Diligence Process and How Should Sellers Prepare?
Due diligence is the process whereby buyers verify your business’s claims regarding its operations, finances, and legal standing. A well-prepared due diligence phase helps avoid surprises and builds buyer trust.
What Does a Seller’s Due Diligence Checklist Include?
A comprehensive checklist should cover: • Financial due diligence: Audited statements, tax returns, cash flow records, and liabilities.
• Legal due diligence: Contracts, intellectual property documentation, employment agreements, permits, and licenses.
• Operational due diligence: Customer contracts, supplier agreements, inventory levels, and production processes.
Having these documents organized and accessible accelerates the review process and enhances buyer confidence.
How Does the Buyer Conduct Due Diligence?
Buyers review the organized documentation with the help of financial advisers, lawyers, and accountants. They may conduct on-site visits and interviews with key personnel to confirm financial and operational realities. The purpose is to verify the valuation and identify any vulnerabilities that could affect future performance or justify a price adjustment.
What Are Common Due Diligence Issues and How Can You Address Them?
Common issues include discrepancies in financial records, unresolved legal matters, incomplete documentation, and operational inefficiencies. Conducting internal audits before initiating the sale helps highlight potential red flags. Address these issues openly with corrective action plans to mitigate any negative impact during negotiations.
How Can You Facilitate a Smooth Due Diligence Process?
Efficiency in due diligence requires clear communication and organized document management—often through a secure data room where information is continuously updated. Establish a direct communication channel for buyer queries and schedule regular updates with your advisers. This structured approach ensures that all parties remain informed and that the due diligence process progresses smoothly.
How Do You Negotiate and Close the Business Sale Successfully?
The negotiation and closing phases are critical in securing a successful sale. Effective negotiation involves a well-prepared presentation of valuation and due diligence documents, along with strategic flexibility during discussions.
What Are Effective Strategies for Negotiating the Sale Price?
Key strategies include:
• Setting a firm yet realistic asking price based on a professional valuation.
• Using market comparables to justify your asking price.
• Remaining flexible on non-price factors, such as payment terms and post-sale support.
• Being prepared to walk away if the terms do not meet acceptable thresholds.
This approach ensures that both the seller’s requirements and the buyer’s concerns are addressed, leading to a mutually beneficial deal.
How Do You Draft and Review the Purchase Agreement?
The purchase agreement records all negotiated terms, including the sale price, payment schedule (often involving escrow arrangements), and the transfer of assets. It should be drafted by an attorney experienced in business sales to ensure compliance with local laws. Sellers must review the agreement carefully to confirm that every term reflects the negotiations accurately, with any ambiguities clarified before signing.
What Steps Are Involved in Closing the Deal?
Closing involves several steps:
• Signing the final purchase agreement.
• Transferring ownership of business assets.
• Completing all financial transactions, such as escrow deposits and final payments.
• Obtaining any required regulatory approvals.
A formal closing meeting, often with legal representatives present, finalizes the deal once all conditions are met.
How Can You Ensure a Smooth Transition Post-Sale?
A seamless post-sale transition benefits both parties. Sellers can offer consulting or training sessions to help the new management maintain operational continuity. Clear communication of operational procedures, supplier contacts, and customer relationships is vital. Proper planning for overlapping contracts and commitments ensures stability for the buyer while preserving the business’s value.
How Long Does It Typically Take to Sell a Business and What Factors Influence Timing?
The timeframe to sell a business can range widely—from as little as three months to over a year—depending on factors such as market conditions, industry type, business size, and preparation. Efficient due diligence and proactive marketing can help shorten the process, while complex deals may require extra time.
What Is the Average Timeframe for Selling Different Types of Businesses?
Generally, small privately held businesses sell faster due to fewer regulatory hurdles and simpler operations. Retail and service-oriented businesses often close within six to nine months, whereas specialized manufacturing or tech companies may take up to a year. Seasonal businesses might experience additional delays, making early preparation essential.
How Do Market Conditions Affect the Sale Duration?
In strong economic climates with high investor confidence, sales are typically faster due to robust buyer interest and higher valuations. In contrast, downturns or market volatility can extend negotiations and due diligence, delaying the final sale.
What Can Sellers Do to Expedite the Sale Process?
To speed up a sale, ensure that all financial and operational documents are accurate and accessible. Address any legal or operational issues in advance, and work with knowledgeable business brokers who understand market dynamics. Maintaining open and consistent communication with interested buyers also helps resolve queries quickly and keeps the process on track.
What Are the Typical Costs Involved in Selling a Business?
Various costs are associated with selling a business. These expenses include brokerage fees, legal fees, accounting fees, due diligence expenses, and marketing costs. Understanding and managing these costs is critical, as they reduce the net proceeds of the sale.
What Fees Should Sellers Expect to Pay?
Sellers should budget for several direct fees:
• Brokerage fees, typically ranging from 5% to 10% of the sale price.
• Legal fees for drafting and reviewing contractual documents.
• Accounting fees for audits and tax consultations.
• Due diligence expenses and costs for preparing marketing materials.
Clear financial planning helps in setting realistic expectations for the final proceeds.
How Do Costs Vary Between Selling Privately and Using a Broker?
Selling privately might save on brokerage fees, but it often burdens the seller with additional self-managed marketing and extended due diligence, which can increase overall costs indirectly. Using a broker, despite requiring an upfront commission, usually provides faster transactions and professional expertise, which can lead to a higher sale price and ultimately justify the expense.
How Can Sellers Minimize Sale-Related Expenses?
To minimize expenses, sellers should streamline financial audits, consolidate legal services, and prepare documentation thoroughly to avoid delays during due diligence. Negotiating fixed-fee legal services or lower commission rates with brokers, along with incremental improvements in operational efficiency, can offset some of these costs and enhance net returns.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What is business valuation and why is it important?
A: Business valuation calculates the economic worth of a company. It is crucial for determining a fair sale price, guiding negotiation strategies, and building buyer confidence by reflecting both current performance and future growth potential.
Q: How should I prepare my financial records before selling my business?
A: Update and audit financial statements, tax returns, cash flow reports, and profit analyses. Clear and transparent documentation reduces buyer uncertainties during due diligence and reinforces credibility.
Q: What is a Confidential Information Memorandum (CIM)?
A: A CIM is a detailed document that outlines key business information—financial data, market analysis, operational specifics, and growth opportunities—while maintaining confidentiality. It serves as a vital marketing tool to attract qualified buyers.
Q: How long does the due diligence process typically take?
A: The process usually lasts between three to six months, depending on the completeness of your documentation and the complexity of the business. Preparing in advance can help expedite this phase.
Q: What are the main negotiation strategies for selling a business?
A: Effective strategies include setting a realistic asking price based on professional valuation, using market comparables to support the price, and being flexible on non-price terms like payment structure and transition support. Clear, well-organized documentation is essential.
Q: What costs should sellers expect when selling their business?
A: Common expenses include brokerage fees (typically 5%-10% of the sale price), legal and accounting fees, due diligence, and marketing costs. Proactive cost management is key to optimizing net sale proceeds.
Q: How can I ensure a smooth transition after selling my business?
A: Offer post-sale support such as training or consulting, document standard operating procedures, and maintain clear communication channels with the new owner to preserve business continuity and value.
Q: What are the key steps to sell your business successfully??
Selling a business is a significant endeavor that requires careful planning and execution to achieve a successful outcome. One of the first key steps in the process is conducting a thorough valuation of the business. Understanding the true worth of the company helps sellers set a realistic asking price and attract potential buyers. This valuation should consider various factors such as revenue, profit margins, assets, and market conditions. Engaging a qualified business appraiser or financial advisor can provide an objective perspective and equip the seller with crucial data to make informed decisions throughout the sale process.
Once the valuation is established, the next vital step is preparing the business for sale. This involves optimizing operations, enhancing financial records, and addressing any potential liabilities. Making necessary improvements not only boosts the business’s appeal but can also increase its overall value. Additionally, creating a comprehensive information package for prospective buyers is essential. This package typically includes an overview of the business, financial statements, operational details, and growth opportunities, enabling potential buyers to make informed decisions. Finally, working with an experienced business broker can streamline the selling process; brokers leverage their industry knowledge and networks to reach a broader audience of potential buyers and facilitate negotiations, making the experience smoother and more effective for the seller. With careful preparation and strategic execution, a business owner can navigate the complexities of selling their business successfully.
Q: How do you prepare your business for a successful sale??
A: Preparing a business for a successful sale involves a strategic approach that ensures maximum value and attracts potential buyers. It begins with a thorough assessment of the company’s financial health. Business owners should clean up their financial statements, making sure they reflect accurate and comprehensive records over the past few years. Engaging a professional accountant to conduct an audit can provide clarity and build trust with potential buyers. This not only enhances the credibility of the financial data but also identifies areas for improvement, allowing for necessary adjustments that can increase the overall valuation of the business.
Additionally, enhancing the business’s operational efficiency can significantly bolster its appeal. Owners should take proactive steps to streamline processes, eliminate inefficiencies, and document standard operating procedures. This showcases a well-functioning operation that can run smoothly without the current owner’s direct involvement, making it an attractive proposition for buyers. Moreover, investing in marketing efforts to strengthen the brand presence can reinforce perceived value, while ensuring that customer relationships are nurtured can lay the groundwork for a seamless transition post-sale. By focusing on these key areas—financial clarity, operational efficiency, and brand strength—business owners can not only prepare for a successful sale but also maximize their potential return on investment.
Factors Affecting Business Sale Timing: Tips to Expedite
Selling a business successfully requires careful planning, diligent preparation, and strategic execution from start to finish. By ensuring an accurate valuation, preparing comprehensive financial and legal documentation, implementing targeted marketing strategies, and managing a smooth due diligence and negotiation process, sellers can maximize their sale value and achieve a seamless transition. These proven steps not only build buyer confidence and reduce risks during negotiations but also lay a solid foundation for future entrepreneurial endeavors.